Wayfinding Solution for Smart Indoor Spaces
As there is no sufficient GPS signal available indoors, the positioning and navigation of people has to be solved in a different way. Get to know full-service solutions for positioning and indoor navigation via BLE beacons.
How it works
How Does Indoor Navigation Work Without GPS?
The Global Positioning System (GPS) needs several satellites’ clear line of sight to work reliably. There is hardly any chance of GPS reception indoors. In addition, you cannot determine which floor of a building you are standing on.
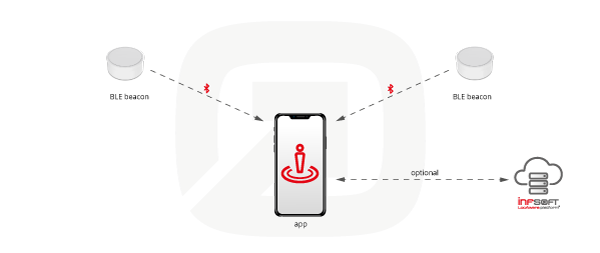
For this reason, other technologies are used indoors. The most common solution is positioning with Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) beacons in combination with smartphone sensors. Using this method, the position of an end device can be determined, and client-based applications such as indoor navigation are made possible.
How to Use Bluetooth Beacons for Indoor Navigation
Beacons have been experiencing a real boom since 2013. Today, there are numerous suppliers of beacon hardware worldwide that work with the popular iBeacon format.
For indoor navigation, beacons are placed at regular intervals in the building. They then regularly transmit signals via Bluetooth that are received by mobile devices (e.g., smartphones). An app on the smartphone interprets the signals, and the position is determined directly on the end device. Beacons cost between about three and 30 euros, have battery lives of several years, and can cover up to 70 meters indoors. The number of beacons required depends on the area and the desired positioning accuracy.
infsoft, a leading provider of comprehensive real-time location systems, offers specialized infrastructure hardware. infsoft Locator Beacons can be used for indoor navigation and simultaneously enable server-based applications such as people or object tracking.
Features
Features of an Indoor Navigation App
Indoor navigation facilitates orientation in complex buildings and on extensive campus areas. A corresponding app can offer numerous functions:
At a glance
2D/3D map
Points of Interest
Favorites and search function
Backchannel (e.g., for push messages)
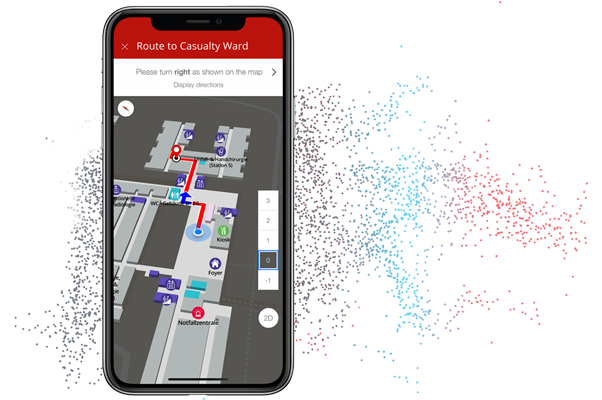
Turn-by-turn directions
“Around me” function
Colleague finder & location sharing
Interfaces to third-party systems
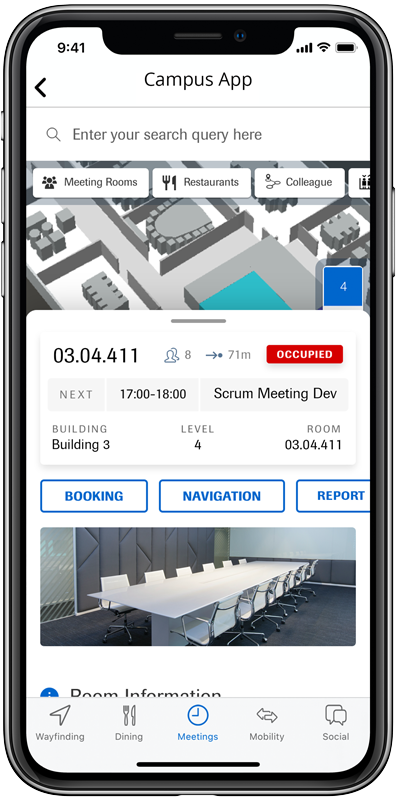
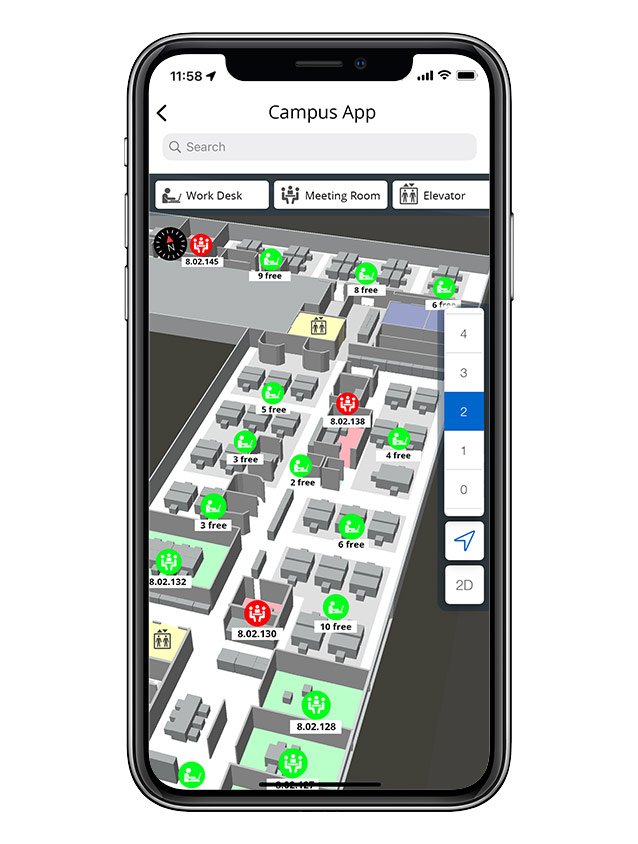
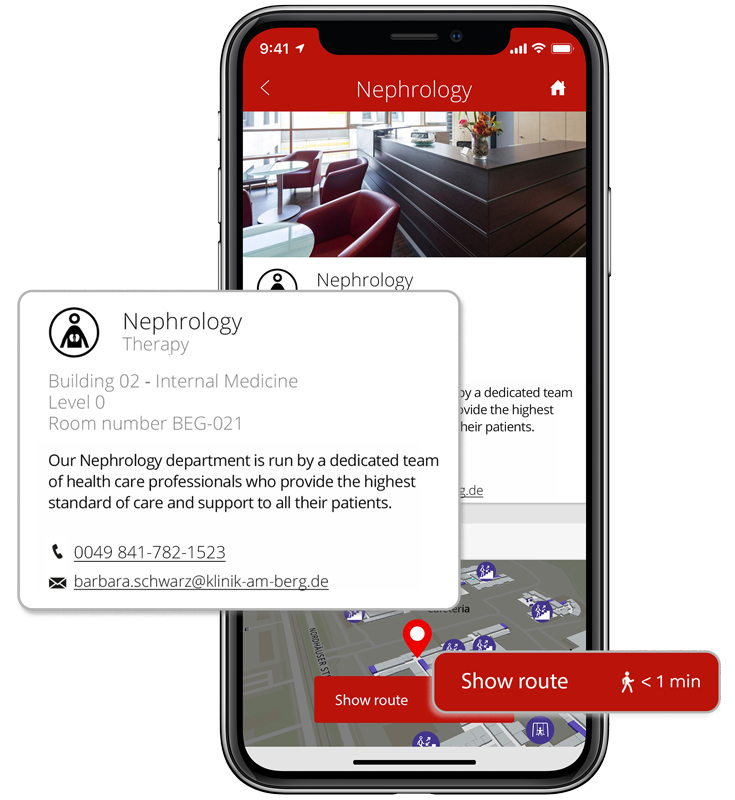
In addition to relevant points of interest (rooms, function areas, sanitary and gastronomic facilities, etc.), the digital map also shows the user’s current location. Users can call up detailed POI information such as opening hours or contact options via the app.
Turn-by-turn navigation guides the users to their destination. The wayfinding starts automatically from the current location of the mobile device. It is also possible to share one’s position with colleagues on site.
Added Value Through Comprehensive Solutions
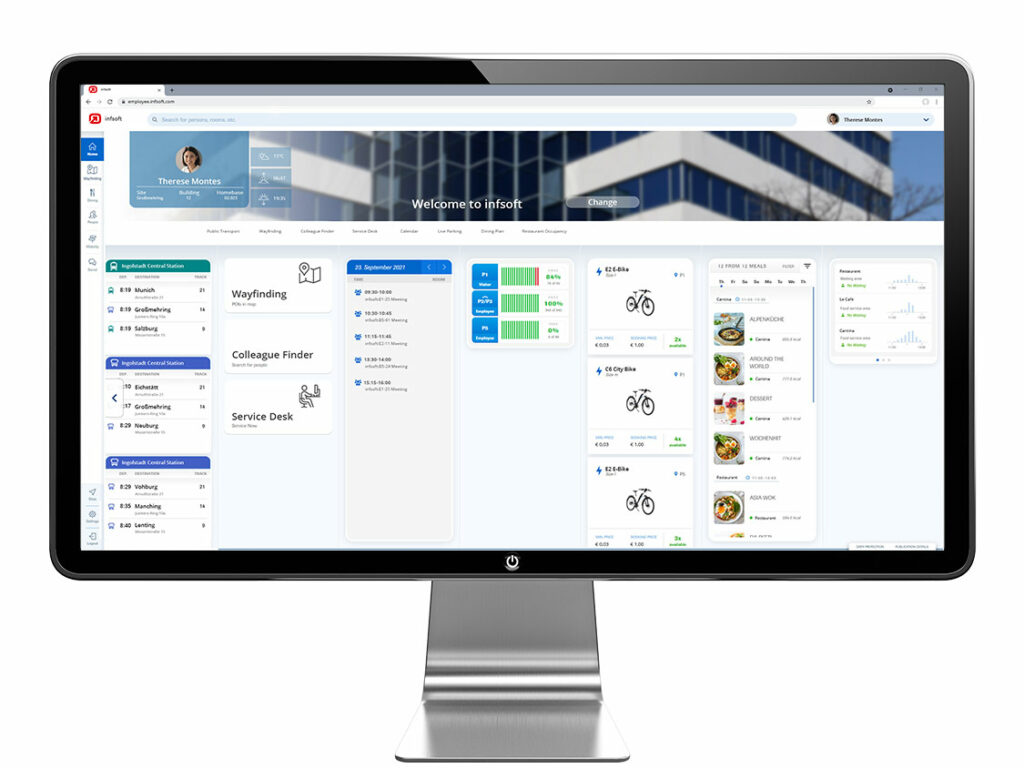
Client-based positioning on the mobile device and indoor navigation can be components of digital applications, but are usually combined with other services to generate higher added value for the user. A good example is a comprehensive employee app for large office buildings and campus areas. It can be equipped with the following features, among others:

Mobility
Travel and mobility information such as public transport timetables, available parking spaces, shuttle timetables, e-bike parking spaces
Wayfinding
Wayfinding within the building, between buildings, and across all floors
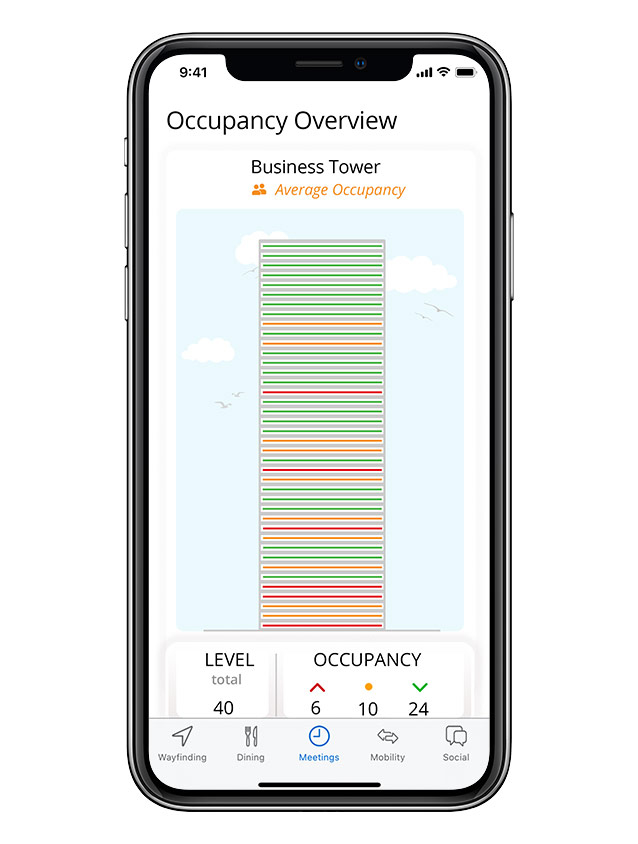
Meetings
Occupancy information and real-time availability, room booking

Networking
Functions to promote internal communication and networking with colleagues (location sharing, skill finder, etc.)
Issue Reporting
Creation of tickets via ITSM software (e.g., ServiceNow), automatic geo-reference or scanning of QR code
Dining
Canteen locations and menus including filter options and utilization information
IMPLEMENTATION OPTIONS

Native App
A native app is downloaded to the mobile device. Beacons installed in the building send out Bluetooth signals that are interpreted by the app and used to calculate the position.
Progressive Web App
A progressive web app is accessible via a web browser. It contains all the functionalities of the native app except for real-time localization. There is no need to install an application on the end device.

Touch Terminal
One or more stationary terminals can be installed at relevant points in the building. The terminal provides an overview of the location and simulates navigation to the selected destination.
Use CAses
What Are Possible Application Scenarios?
Indoor navigation is particularly helpful for orientation in complex buildings, such as train stations, airports, hospitals, or large industrial and office areas. In addition to indoor navigation, a corresponding app can offer other services such as room booking, workflow management, location sharing, and much more. Here are some use cases for indoor navigation and related services:
infsoft solutions
Which Solutions Does Full-Service Provider infsoft Offer?
infsoft provides enterprise customers with a comprehensive portfolio of digital products and solutions. Indoor navigation is a component of two of these products:
infsoft Wayfinding
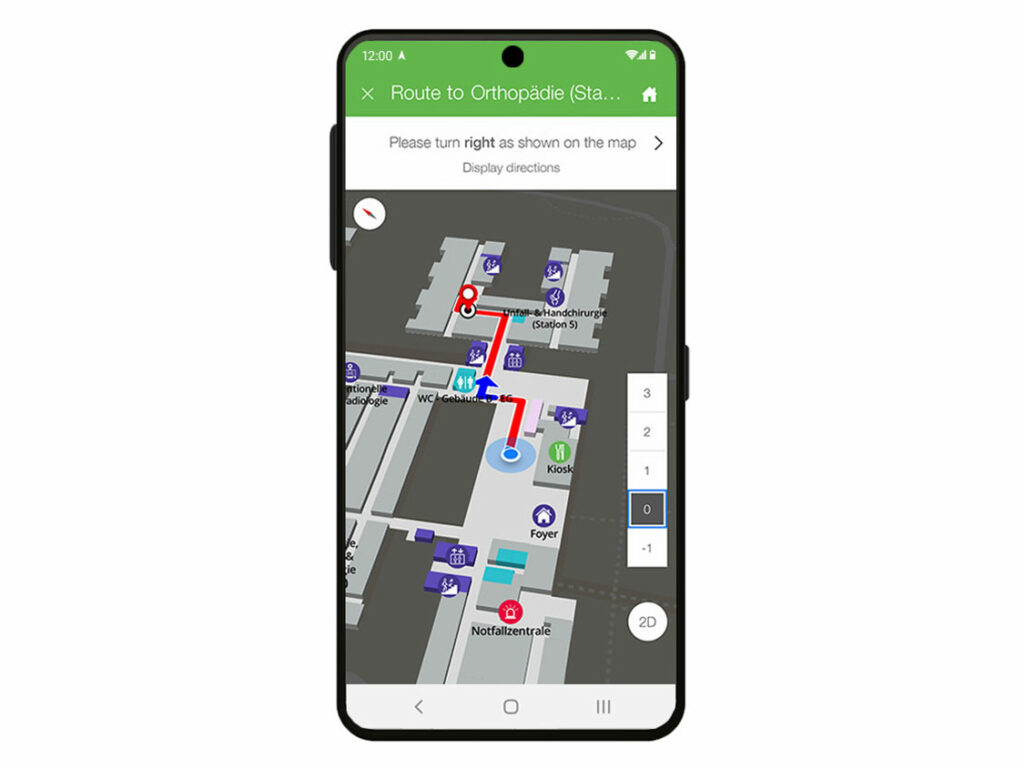
infsoft Wayfinding assists users in reaching their desired location quickly and easily. The product can be used indoors and outdoors in buildings such as hospitals, airports, and office complexes. The solution includes a map of the location, which provides an overview of the site. In addition, points of interest (POI) can be found directly on the map as well as via a search bar, and the shortest route to them can be displayed. On mobile devices, the app can also provide real-time turn-by-turn navigation to further support the user.
Impressions of infsoft wayfinding
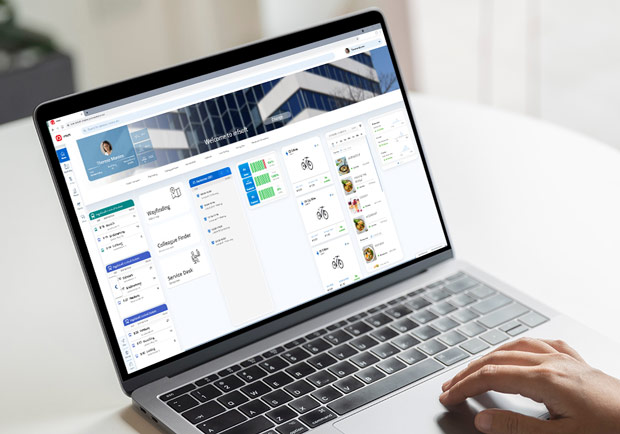
infsoft Workplace Experience
A Workplace Experience app can incorporate many other features in addition to an indoor navigation solution. These include occupancy information, room booking and planning of meetings, issue reporting, functions for networking with colleagues, and much more. The solution can be customized to meet the needs of the individual client.